2019-10-23 04:26:12
Throat cancer often doesn’t cause symptoms until later stages—yet early detection makes for more effective treatment. If you notice any of the following throat cancer symptoms, or if you have a history of smoking or excessive alcohol use, call your doctor.
What is throat cancer?
Cancer is a class of diseases in which abnormal cells multiply and divide uncontrollably in the body. These abnormal cells form malignant growths called tumors.
Throat cancer refers to cancer of the voice box, the vocal cords, and other parts of the throat, such as the tonsils and oropharynx. Throat cancer is often grouped into two categories: pharyngeal cancer and laryngeal cancer.
The cause of throat cancer
Palate is the highest part of the throat. Currently, scientists have not been able to determine the exact cause of this type of cancer. Some studies show that people infected with Epsstein - Barr virus are at higher risk of getting throat cancer.
Although the exact cause is not known, people who drink a lot of alcohol, smoke cigarettes or eat a variety of fermented foods like pickles are susceptible to this dangerous type of cancer.
Palate cancer occurs at any age but most commonly in men from 40 to 60 years old.
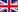
The signs of nasopharyngeal cancer are often vague so are easily overlooked.
Symptoms you may have:
- Voice changes like cracking or hoarseness
- Trouble swallowing or breathing
- Sore throat, cough, or earache that won’t go away
- Headache
- Neck lump
- Unexplained weight loss
- See your doctor right away if any symptoms last for more than a few weeks.
What Puts You At Risk?
- Using tobacco for a long time. Smoking it and chewing it are the biggest risk factors for all head and neck cancers, including throat cancer.
- Drinking heavily and regularly. That means more than two drinks of alcohol a day if you're a man or more than one a day if you're a woman.
- You drive up your risk even more if you drink and you smoke.
- HPV. Human papillomavirus is linked to cancers in the back of the throat, including tongue and tonsil cancers. You can help protect your kids from it in the future by having your children get the HPV vaccines. Kids should start the series of shots between 11 and 12 years old.
Other risk factors include:
- Gender. Men are five times more likely to get it than women.
- Age. Most people get diagnosed after 65.
- Race. African-American men are at the biggest risk.
- Chemical exposure. This includes being around asbestos, nickel, and sulfuric acid fumes.

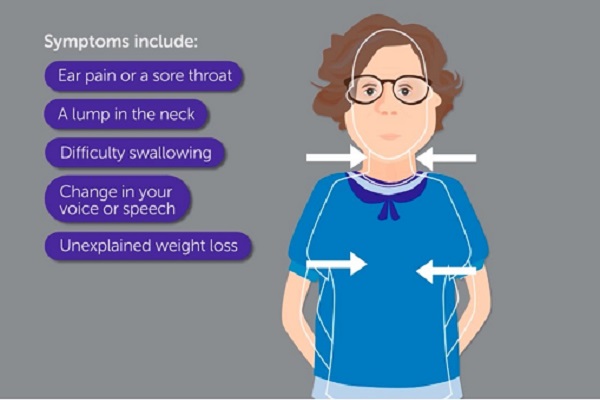
Different Types
Most types grow in the flat, thin cells that line the throat and voice box.
Doctors identify them by where they are:
- Nasopharynx. This is the upper part of your throat behind your nose. In the U.S, cancer here is rare.
- Oropharynx. This part is behind your mouth. Cancer is most likely to grow in the tonsils, the back of the tongue, or the soft palate.
- Hypopharynx. That's the narrow area behind your voice box.
Cancer can grow in the three parts of the voice box itself:
- Glottis. This holds your vocal cords.
- Supraglottis. This is the area above the glottis.
- Subglottis. This is the area below your vocal cords and above your windpipe.
Getting a Diagnosis
Your doctor will examine you and ask about your general health, smoking and drinking habits, and sexual history. He might use devices to get a closer look at your throat.
If the doctor thinks you may have cancer, he’ll order tests and procedures depending on what kind he suspects. Common ones include:
- A biopsy collects a tissue sample that gets examined under a microscope to look for cancer cells. It’s the only way to know for sure if a tumor is cancer and what kind it is. The procedure may be done with surgery, fine needles, or an endoscope -- a flexible tube with a camera that’s lowered into the throat through your nose or mouth. A tool on the end will take the biopsy.
- Imaging tests can help doctors find a tumor. They can also show how big it is and if it has spread. These include:
- MRI or CT scan
- PET scan
- X-rays
If cancer of the oropharynx is found, the sample may be tested for HPV. Usually, someone's health outlook is better if their disease tests positive for this virus rather than being smoking-related cancer.
Treatment of throat cancer
Depending on the stage of the disease, the doctor recommends the appropriate treatment regimen. However, the most popular treatments for nasopharyngeal cancer are radiation therapy and chemotherapy. For patients with advanced throat cancer, the treatment is only meant to improve the quality of life for the patient.
Patients should eat liquid food, easy to swallow but ensure nutrients.
After performing radiotherapy or chemotherapy, patients should regularly practice opening their mouth and massaging the neck to reduce the side effects of the above treatments.
According to a 2010 US study, the number of survivors after 5 years found palate cancer in stage 1 was 72%, detected in stage 2 was 64%, detected in stage 3 was 62% and in stage 4 is 38%. However, depending on the condition and psychology of patients that their life time may vary.
How to prevent and avoid throat cancer
Because the cause of the disease is not known, it is very difficult to provide the best preventive measures. However, based on the subjects who are often those who drink, smoke or eat fermented foods, we can prevent throat cancer with some notes:
- Men should not smoke cigarettes, pipe tobacco, limit drinking alcohol and alcoholic beverages to reduce the risk of cancer of the throat.
- Limit eating fermented foods such as pickles, salted fish, tomato ... Enhance exercise, sports to improve health.
- Smoking cigarettes increases the risk of throat cancer.
For appointment or screening service consultation, please contact:
- Ms. Võ Thị Mỹ Liên: (8428) 6280 3333, ext. 8424
- Ms. Nguyễn Thị Lệ: (8428) 6280 3333, ext. 8402
For any further information about medical services provided by City International Hospital, please contact:
- Operator: (8428) 6280 3333, ext. 0
- Address: Level 3, No. 3, 17A Street, Binh Tri Dong B Ward, Binh Tan Dist. (Next to AEON Mall Binh Tan). Ho Chi Minh City.
- Website: https://cih.com.vn/en/
- FB page: https://www.facebook.com/BenhVienQuocTeCity